This is an intelligent way to replace an undesirable object
in a picture by its surrounding pixels using GIMP:
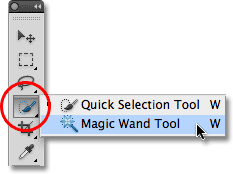
- use the magic wand or lasso tool to select area to be removed (click Strg key to add areas as necessary)
- chose Select → Grow → 1 pix (if needed)
- then use either:
- Clone tool
- or Filters → Map → Resynthesize…
- or Filters → Enhance → Heal selection…
- Specify the radius to take the selection from. The default is 50
and should work fine. If it doesn’t, play around with the radius until you get
the desired result.
- chose Shift+Strg+A to unselect area
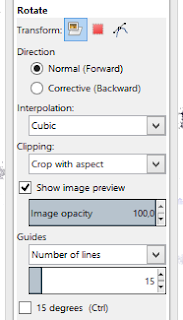
Rotate Image:
- Select the relevant area
- Press Shift+R
- Click with the mouse anywhere on the image to bring up the input window
- Press or chose "Rotate"
Perspective Tool:
Helpful
video for using Shift+P. Make sure here to always use "Corrective (Backward)" option.